“Egg” a super-food
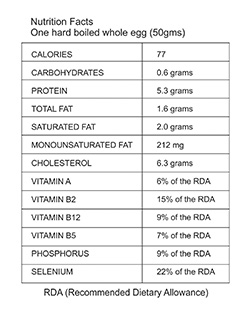
Eggs are one of the superfoods which provide high quality and a good amount of protein as well as calcium, iron, vitamins A & Phosphorus, zinc, iodine, iron, and essential fatty acids.
There’s a lot of debate about whether to eat the whole egg or just the egg white. The truth is that, although there are nutrients in egg whites, most nutrients are found in the yolk. However, egg yolks also contain more calories and saturated fat. The whites, on the other hand, are high in protein content which can help suppresses your appetite, as it makes you feel fuller for a longer time which can bring you closer to your weight loss goals.
The egg white is more than 50% of water. The rest of the egg white is mostly albumin, which makes up the majority of the protein found in the egg white but there are others as well including globulins that have immune effects.
As a high-protein food, egg whites boast a high nutritional value and has just a few calories per serving. Studies indicate that regular consumption of egg whites may reduce cholesterol levels and lower the risk of arteriosclerotic diseases in as little as eight weeks
Having a good amount of protein is also important for maintaining and building muscle, especially if you’re trying to lose weight and gaining muscles.
However, Full eggs provide you with some more protein but due to high fat, it will also provide extra calories. Egg whites can be an appealing choice for people who are trying to lose weight.
One cup of egg whites provides approximately 117 calories, 1.8 grams of carbs, 0.4 grams of fat, and a whopping 26.5 grams of protein. It also delivers 63 percent of the recommended daily intake of riboflavin, 4 percent of the RDA of vitamin B-12, and 69 percent of the RDA of selenium. Furthermore, egg whites are rich in potassium and sodium, which helps prevent electrolyte imbalances.
Egg whites have all 9 non-essential amino acids. (non-essential amino acids are not made in the body)
Glutamine:
Glutamine is an energy source for intestinal and immune cells. It also helps maintain the barrier between the intestines and the rest of your body and aids with the proper growth of intestinal cells.
Glutamine also acts as a recovery agent, promoting muscle repair. It also helps in preventing muscle breakdown during sickness and when you are training.
Proline:
Proline is an important nonessential amino acid that’s responsible for cellular regeneration, tissue repair, and collagen-building. It has beneficial cardiovascular properties, working to support balanced blood pressure levels and arterial elasticity.
Alanine:
Alanine is an amino acid that is used to make proteins. It is used to break down tryptophan and vitamin B6. It is a source of energy for muscles and the central nervous system. It strengthens the immune system.
Arginine:
it is most commonly used for recovery after surgery, heart and blood vessel conditions, such as angina pain and high blood pressure. It is also commonly used in pregnancy complications caused due to high blood pressure.
L-arginine:
L-arginine is converted in the body into a chemical called nitric oxide, which causes improved blood flow by widening the blood vessels. L-arginine stimulates the release of growth hormone-like insulin and other substances also.
Lysine:
It helps in improving cold sores, reducing blood pressure, promotes collagen growth. It helps the body in absorbing calcium, iron, and zinc. It supports the immune system of our body and also helps In producing enzymes, antibodies, and hormones.
Histidine:
Histidine facilitates growth, the creation of blood cells, and tissue repair. It also helps maintain the special protective covering over nerve cells, which is called the myelin sheath. The body metabolizes histidine into histamine, which is crucial for immunity, reproductive health, and digestion. Histidine is also used by the body to make specific hormones and metabolites that impact kidney function, the transmission of nerves, stomach secretions, and the immune system.
Serine:
serine is known to have numerous benefits for proper human body functioning… Serine makes up brain proteins and nerve coverings. Serine supports in the production of immunoglobulins and antibodies. Serine is also required in the production of the amino acid called tryptophan, which is imperative to the construction of other important neurotransmitters. Tryptophan plays a very important role in the making of serotonin. And is a natural relaxant, relieves stress, anxiety, and depression. That’s why decreased levels of serine not only do we lose the direct benefit of serine alone, but we will also miss out on the many benefits of tryptophan and serotonin.
Valine:
Valine is one of three branched-chain amino acids, it helps stimulate muscle growth and regeneration and is involved in energy production.
Tryptophan:
Tryptophan, for instance, is an essential amino acid that regulates your mood and appetite. It promotes relaxation and protects against anxiety, depression and high blood pressure.
The myth about eggs:
There is a popular myth that eating eggs in summer can be unhealthy as they have a tendency to produce heat in our body and can cause indigestion and discomfort.” Though it is completely okay to have eggs in summer, but in moderation. Eggs may cause heat in the body which further may lead to bowel issues, but if eaten more than advised. It is advised that you can eat 1 to 2 eggs a day for a non-athletic person but an athlete or a bodybuilder/powerlifter etc. can have 3-5 eggs a day with limited egg yolks depending on a fitness goal and health conditions. And not more than that as it may cause your body to heat further leading to bowel problems.
Egg allergy:
Eggs are one of the most common allergy-causing foods for children. symptoms usually occur a few minutes to a few hours after eating eggs or foods containing eggs. Signs and symptoms range from mild to severe and can include skin rashes, hives, nasal congestion, and vomiting or other digestive problems. Rarely, egg allergy can cause anaphylaxis — a life-threatening reaction.
Egg allergy can occur as early as infancy. Most children, but not all, outgrow their egg allergy before adolescence.
Some of the symptoms are:
· Skin inflammation or hives — the most common egg allergy reaction
· Nasal congestion, runny nose, and sneezing (allergic rhinitis)
· Digestive symptoms, such as cramps, nausea, and vomiting
· Asthma signs and symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, chest tightness or shortness of breath
Anaphylaxis:
An acute allergic reaction can lead to anaphylaxis, a life-threatening emergency.
It’s signs and symptoms include:
· Constriction of airways, including a swollen throat or a lump in your throat that makes it difficult to breathe
· Abdominal pain and cramping
· Rapid pulse
· Shock with a severe drop in blood pressure, felt as dizziness, light-headedness or loss of consciousness