Benefits of core training
To understand the benefits of core training, you need to understand the core muscles.
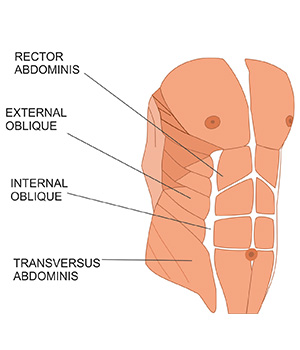
Core muscles consist of six muscles:
- Rectus abdominis
- Internal and external oblique
- Transverse abdominis
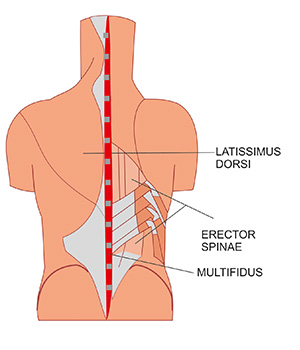
- Erector spinae
- Pelvic floor
- Multifidus

The Benefits of Core Training: Strengthen Your Core for a Stronger Body
A strong core is the foundation of a well-balanced, functional body. Core training goes beyond achieving a toned midsection—it plays a crucial role in improving posture, enhancing athletic performance, preventing injuries, and supporting daily activities. Whether you’re an athlete, fitness enthusiast, or someone looking to improve overall strength, core training is essential.
In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of core training, break down the key muscles of the core, and provide two effective exercises for each muscle group.
Why Core Training Is Important
Core training strengthens the muscles that stabilize the spine and pelvis, allowing you to move efficiently and prevent injuries. Here are some key benefits:
- Improves Posture – A strong core helps maintain proper spinal alignment, reducing back pain and improving overall posture.
- Enhances Athletic Performance – Most sports require core strength for stability, power, and coordination.
- Prevents Injuries – A weak core can lead to compensatory movements, increasing the risk of injuries in the lower back and other areas.
- Supports Functional Movements – Everyday activities such as bending, lifting, and walking rely on core stability.
- Boosts Balance and Stability – Core strength enhances balance, reducing the likelihood of falls and improving movement efficiency.
- Enhances Breathing and Endurance – A strong core supports better breathing mechanics, improving stamina and endurance.
Key Core Muscles and Their Functions
The core is more than just the abs—it consists of multiple muscle groups that work together to provide strength and stability. Below, we’ll break down each muscle’s function and provide two effective exercises for strengthening them.
1. Rectus Abdominis (Six-Pack Muscles)
Function:
- Flexes the spine
- Helps in bending forward and performing crunching movements
Exercises:
- Crunches – Lie on your back, bend your knees, and lift your shoulders towards the ceiling while engaging your core.
- Leg Raises – Lie flat and lift your legs while keeping your lower back pressed against the floor.
2. Transverse Abdominis (Deep Core Muscle)
Function:
- Acts as a natural weight belt, stabilizing the spine and pelvis
- Supports deep breathing and core compression
Exercises:
- Dead Bug – Lie on your back with arms and legs extended. Lower opposite arm and leg while keeping your core engaged.
- Plank Hold – Maintain a forearm plank position while engaging the deep core muscles.
3. Internal and External Obliques (Side Abs)
Function:
- Allows rotational movements of the torso
- Helps with bending side to side
Exercises:
- Russian Twists – Sit with knees bent, lean back slightly, and rotate your torso side to side while holding a weight.
- Side Plank Hip Dips – Hold a side plank and lower your hip towards the floor, then raise it back up.
4. Erector Spinae (Lower Back Muscles)
Function:
- Extends and stabilizes the spine
- Supports upright posture
Exercises:
- Superman Hold – Lie on your stomach and lift your arms and legs simultaneously while engaging the lower back.
- Good Mornings – Stand with a slight bend in your knees, hinge at the hips, and lower your torso while keeping your back straight.
5. Quadratus Lumborum (Side Lower Back Muscle)
Function:
- Provides lateral stability to the spine
- Helps with side bending and back extension
Exercises:
- Side Bend with Dumbbell – Hold a dumbbell in one hand and bend to the side while keeping your core engaged.
- Suitcase Carry – Carry a heavy weight in one hand and walk while keeping your torso upright.
6. Multifidus (Deep Spine Muscle)
Function:
- Stabilizes the vertebrae
- Supports spinal movement and posture
Exercises:
- Bird Dog – Get on all fours and extend opposite arm and leg while keeping your spine neutral.
- Bridge Hold – Lie on your back and lift your hips while squeezing your glutes and keeping your core engaged.
7. Pelvic Floor Muscles
Function:
- Supports the bladder and reproductive organs
- Assists in core stability and posture
Exercises:
- Kegels – Squeeze and hold the pelvic floor muscles for a few seconds before releasing.
- Glute Bridge – Strengthens the pelvic floor while also working the glutes and core.
8. Diaphragm (Core Breathing Muscle)
Function:
- Plays a major role in breathing
- Supports intra-abdominal pressure for core stability
Exercises:
- Diaphragmatic Breathing – Place one hand on your stomach and breathe deeply, expanding your belly rather than your chest.
- Blowout Planks – Exhale fully while holding a plank to engage the diaphragm and deep core.
Final Thoughts
Core training is an essential component of a strong, functional, and injury-free body. By targeting all the key core muscles, you can improve your athletic performance, prevent injuries, and enhance overall movement efficiency.
Start incorporating these exercises into your routine to strengthen your core and experience the benefits firsthand. For more fitness tips and workout guides, follow us at www.fittoflaunt.com.